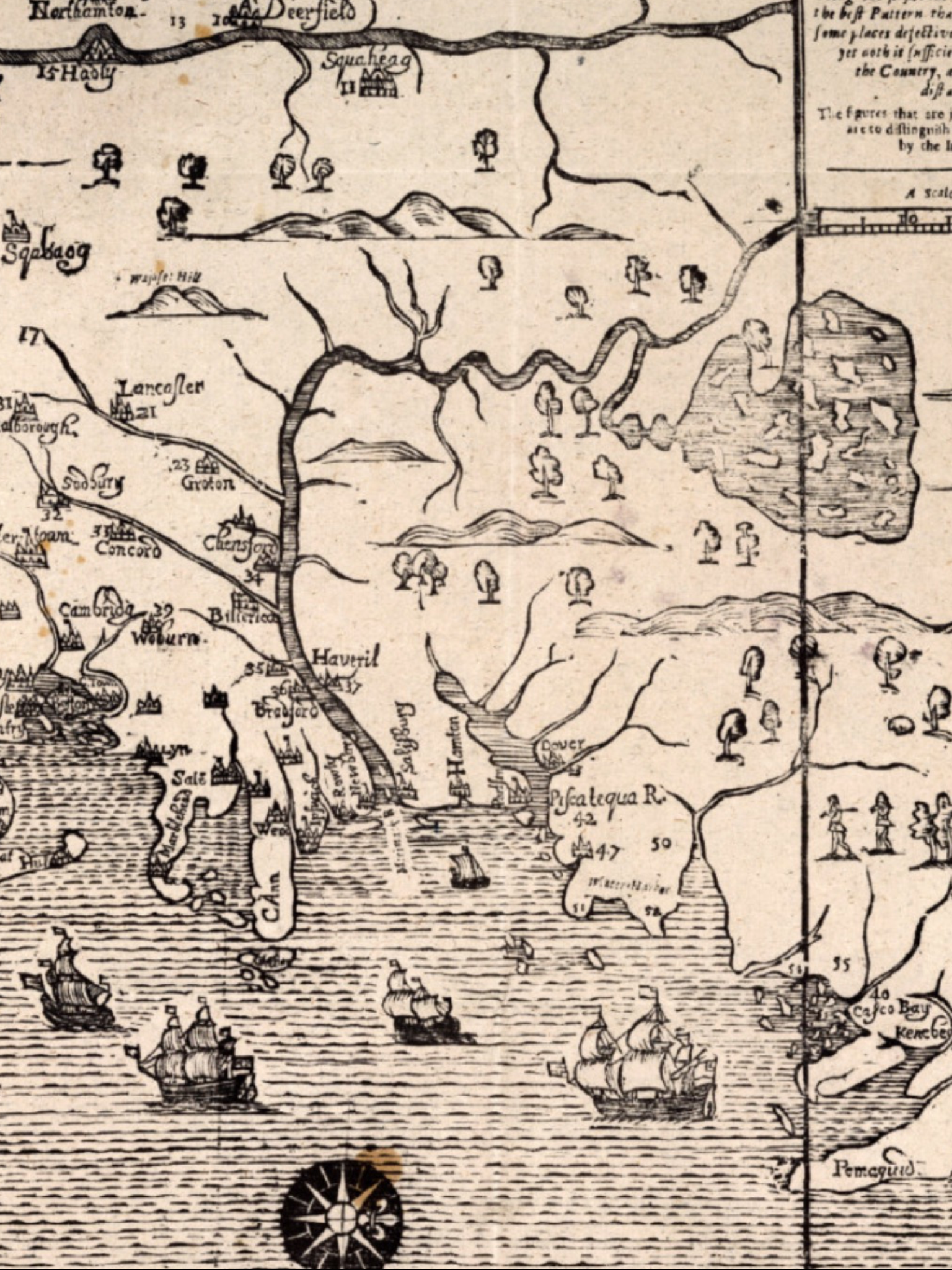
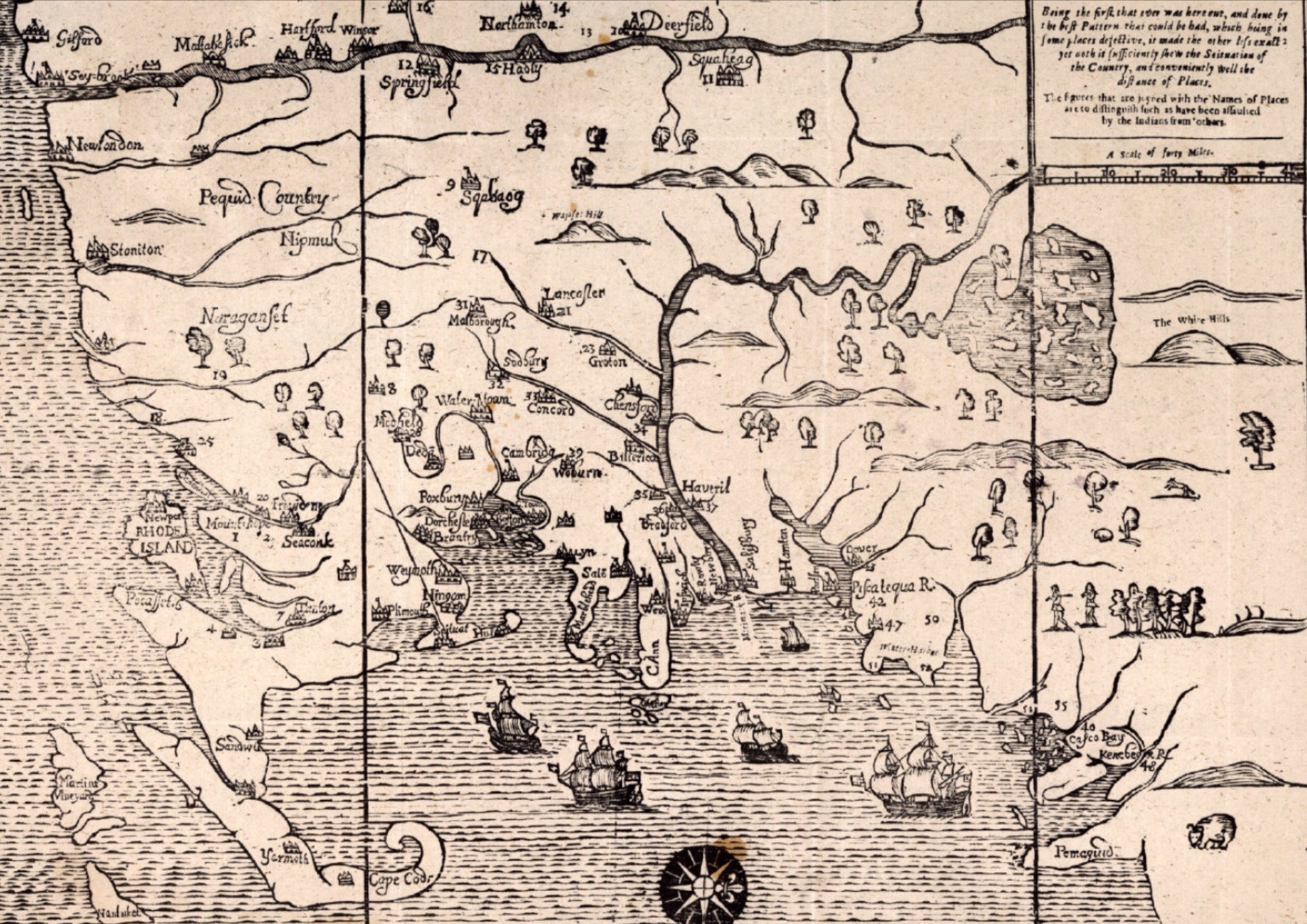
On February 22, 1698 a group of Abenaki warriors raided Andover, Massachusetts and killed five people and two more (Haynes and Ladd) in Haverhill. Raids like this were somewhat common in the Merrimack River Valley at that time, as it was the frontier and friction between settlers encroaching on the lands of Native Americans who had lived there for generations was an unpleasant reality for everyone living in this area. What was particularly interesting about this raid was who they killed, which leads to why they chose this place for a raid in the first place.
Two years earlier at Fort William Henry in Pemaquid, Maine, Captain Pasco Chubb commanded a garrison of 60 soldiers who were stationed here, tasked with defending this relatively new stone fort from the French and Abenaki who would prefer to have them elsewhere. This site, on a point of land jutting out into Johns Bay at the mouth of the Pemaquid River, wasn’t particularly strategic, but it represented what was meant to be a permanent foothold on the coast of Maine (then part of Massachusetts) and the northernmost settlement by the English. Fort George, A wooden stockade on this spot hadn’t fared well just a few years earlier, so in reconstructing the fort the British stepped in and built it of stone and armed it with 15-20 cannon. It was completed in 1692 and held by a garrison of 60-90 men.
There were at least three critical weaknesses with Fort William Henry. First, it was isolated and any reasonable hope for reinforcements was small. Second, the small stone and lime walls were not particularly strong, making them vulnerable to the cannon the French would bring. And third, and an unforgivable mistake given the other vulnerabilities, the supply of drinking water was outside the fort walls! So a siege of any length would prove highly effective as water in the fort was depleted.
Ongoing tensions with the French and Native American population almost guaranteed that a siege would eventually take place. And Fort William Henry was indeed besieged on August 14, 1696 by 100 French and 400 Abenaki. Prior to the siege, two Abenaki chiefs named Edgeremet and Abinquid went to meet with Captain Chubb under a white flag to inquire about some fellow Abenaki captured by Chubb’s predecessor and shipped to Boston. The goal was a prisoner exchange with the British. Chubb and his men raised their guns and shot Edgeremet and two of his sons. Depending on the account you read, Chief Abinquid may have escaped. Either way this act of cowardly violence against Abenaki tribal leaders under a white flag enraged the besiegers. They wouldn’t forget Chubb and the British betrayal.
The Abenaki wrote a letter that demonstrated their rage and feelings of betrayal. It would set the table for later violence against settlers:
“Lord who write at to me, listen and understand what I am about to say, аnd write, to you. Thou wilt easily recognize my words, and why wilt them not recognize them. It is thou (so to express myself) that furnishest them to me. Writing with too much haughtiness, thou obligest me to reply to thee in the same style. Now, then, listen to the truths I am about to tell thee of thyself; of thee, who dost not speak the truth when thou sayeth that I kill thee cruelly. I never exercise any cruelty in killing thee, [a*I kill thee] only with hatchet blows and musket shots. Thy heart must have been еvеr addicted to wickedness and deceit. No other proof is necessary than the acts last autumn at Saco and Pemkuit, taking аnd detaining those who were going to obtain news from thee. Never in the universal world has it been seen, never has it been related of a man being taken prisoner who bears a flag [of truce] and goes to parley on public business. This, however, is what thou hast done; in truth, thou bait spoiled the subject of discussion. Thou hast covered it with blood; as for me, I could never resolve to act in that manner, for therein I have even an extreme horror of thy unparalleled treachery. How then dost thou expect that we would talk. What thou sayest I retort on thyself. There, repent and repair the grave fault thou hast committed; seize those who killed me at Saco, and made me prisoner at Pemkuit. I will do the like by thee. I will bring thee those who killed thee when I shall be able to find them. Fail not to do what I require of thee; of this, I say, who killest me without cause; who takest me prisoner when I am off my guard. – Abenaki letter, written by French missionary brothers Vincent and James Bigot, in response to the treachery at Pemaquid
The French weren’t as surprised, writing in an account of the events that day that “It is to be hoped that the Abenakis will not place any confidence hereafter in English promises.”
The English were disgusted with Chubb for quickly surrendering the fort and fleeing back to Boston. He was thrown in jail for months when he was set free, and only freed when he wrote a petition to the Court. In it he wrote the following:
“And whereas ye petition is a very poore man, having a wife and children to look after with by reason of his confines & poverty are reduced to a meane and necesstous condition, having not wherewith all either to defray his prison necessary charges or to relieve his indigent family…”
Chubb would indeed be released from jail and return to Andover to be with his wife and child. It was there that a party of 30 Abenaki warriors led by Chief Escumbuit from Big Island Pond would become reacquainted with Pasco Chubb, killing his wife and child, and paying extra attention on Chubb, shooting him several times to ensure he was dead. Sweet revenge, perhaps, but with the loss of innocents as well. Chubb has largely been forgotten in the early colonial history of America, and when his name is mentioned it’s appropriately with distain.